Buy a Variety of Concrete Screw Lengths
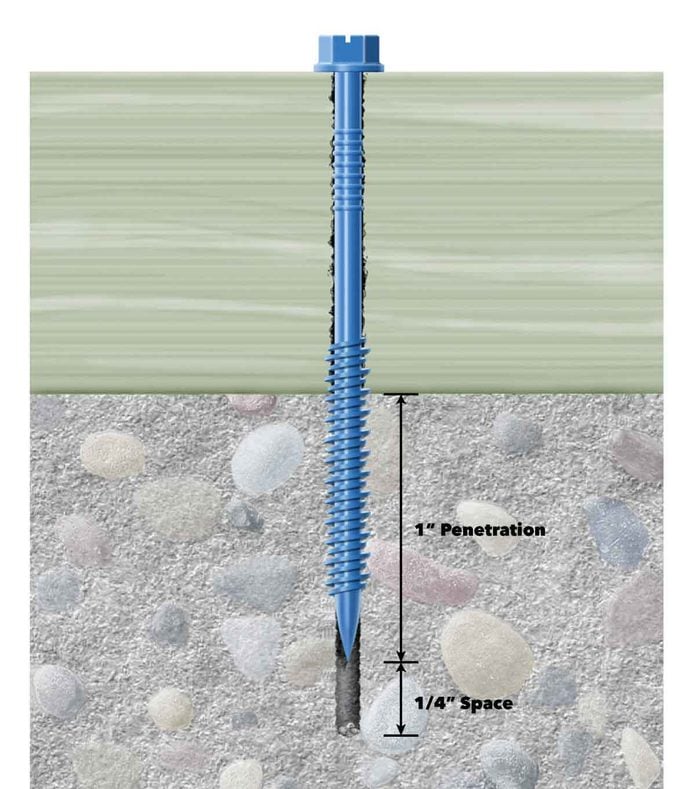
Buy a variety of lengths so you have the correct screw size on hand. Select a screw length to penetrate the concrete at least 1 in. Add 1 in. to the thickness of the material you’re attaching to get the minimum length of screw needed. In hard, dense materials like concrete or stone, this minimum 1-in. screw embedment will work fine. But for maximum strength, use longer screws, up to 1-3/4 in. embedment, in soft brick or other less dense materials. You may have to experiment with a few different lengths to find a screw that you can drive fully and that holds securely.
You’ll find blue concrete screws at home centers, hardware stores and lumberyards, or you can order them by phone or on-line. Screws are available in several lengths in packages of 8 or 25 and in boxes of 100. The more you buy the cheaper the price. A drill bit is usually included in boxes of 25 or more. It’s worth having a couple of screw sizes on hand if you do a lot of projects.
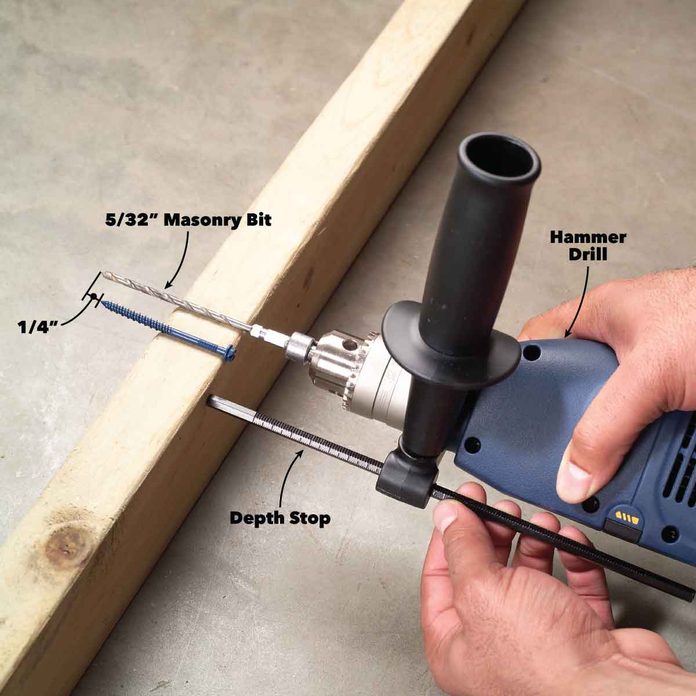
Make Sure to Drill the Hole Deep Enough
Holes for concrete screws should be at least 1/4 in. deeper than the screw will penetrate to allow a little extra space for dust accumulation from the drilling process. See the illustration above. But it’s not always easy to judge how deep you’re drilling. Too shallow and the screw won’t go in. And drilling deeper than necessary is a waste of time and effort. That’s why most hammer drills come equipped with an adjustable depth stop.
Troubleshooting
If you’re having trouble driving the screw all the way, first make sure the hole is deep enough. If it is and you’re still having trouble, there’s probably too much grit in the hole. Remove the screw and clean out the hole by running the bit in and out a few times. Try driving the screw again. If it’s still stubborn, back it out and redrive it a few times. If all else fails, install another screw a few inches away. Finally, consider a little shorter screw for the rest of the holes.
Sometimes you’ll have the opposite problem. The screw will spin without gripping. If this happens, the material you’re fastening to is probably too soft or crumbly. Try a longer screw, or if you’re using a 3/16-in. screw, try a 1/4-in. diameter. You may have to use a concrete anchor that expands as you tighten the fastener.
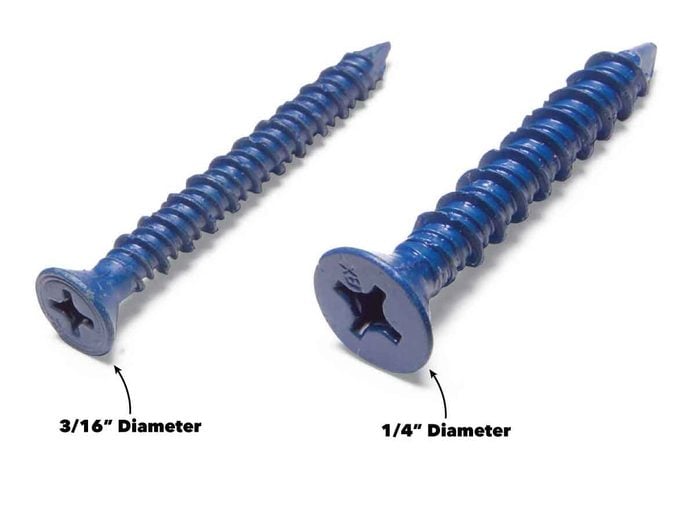

Choose 3/16-in. Screws for Most Light- to Medium-Duty Tasks
Home centers and hardware stores stock concrete screws in two diameters, 3/16 in. and 1/4 in. The 3/16-in. diameter screws are plenty strong for most home tasks like installing furring strips, screwing down walls to concrete floors, and attaching hardware to block or brick. And since they’re a little cheaper and the smaller hole is easier to drill, the 3/16-in. size is usually the better choice. If you’re having trouble with the 3/16-in. screws snapping off because the concrete is too hard, switch to stronger 1/4-in. diameter screws instead. You could also keep some 1/4-in. screws handy in case you strip out the hole for a 3/16-in. screw. Switch to 1/4-in. screws for heavy-duty work like securing a wall cabinet to a concrete or block wall, or supporting shelving that will hold a lot of weight.
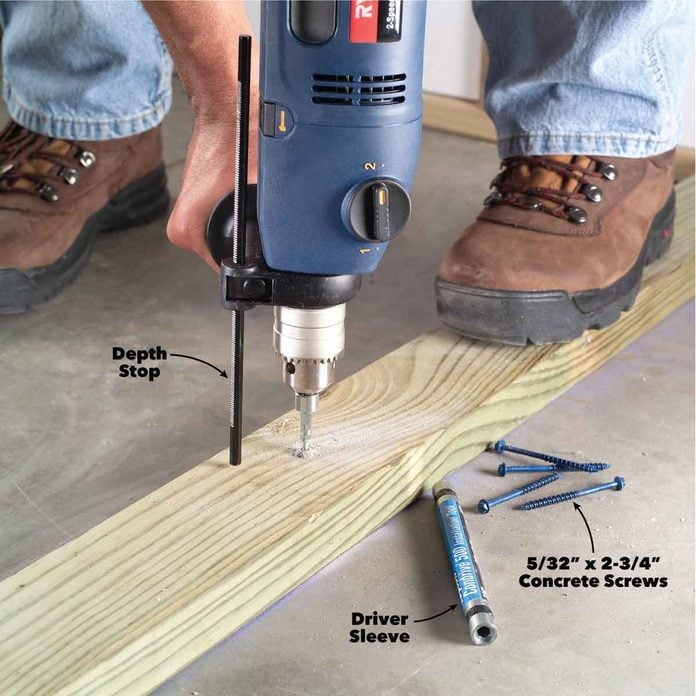

Use a Hammer Drill
In some less dense materials like soft brick, you can drill pilot holes using a carbide-tipped bit in a regular drill. But in most cases, you’ll need a hammer drill. Corded hammer drills cost $65 to $400, or you can buy a cordless model starting at $230. You can also rent hammer drills for about $35 per day.
Precisely sized carbide-tipped bits are often included with packs of screws, or you can purchase one separately. Match the bit to the size screw you’re using: 5/32-in. bit for 3/16-in. screws and 3/16-in. diameter bit for 1/4-in. Keep a spare bit on hand, since the tip can wear out rapidly in some hard materials, resulting in a hole that’s too small. One indication of a worn bit is screws that are difficult or impossible to drive completely.
Close-Up of a Concrete Bit
Concrete bits have a super-hard carbide tips.
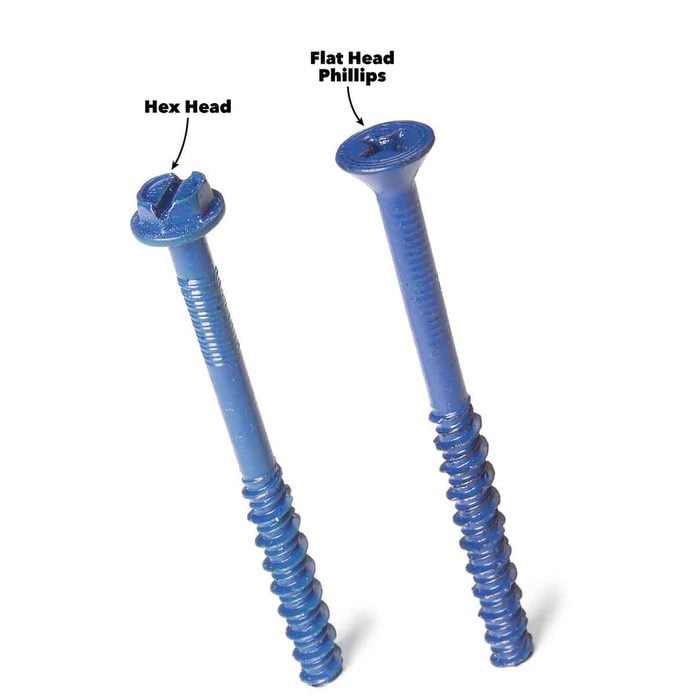

Use Hex Head Screws Where Appearance Isn’t an Issue
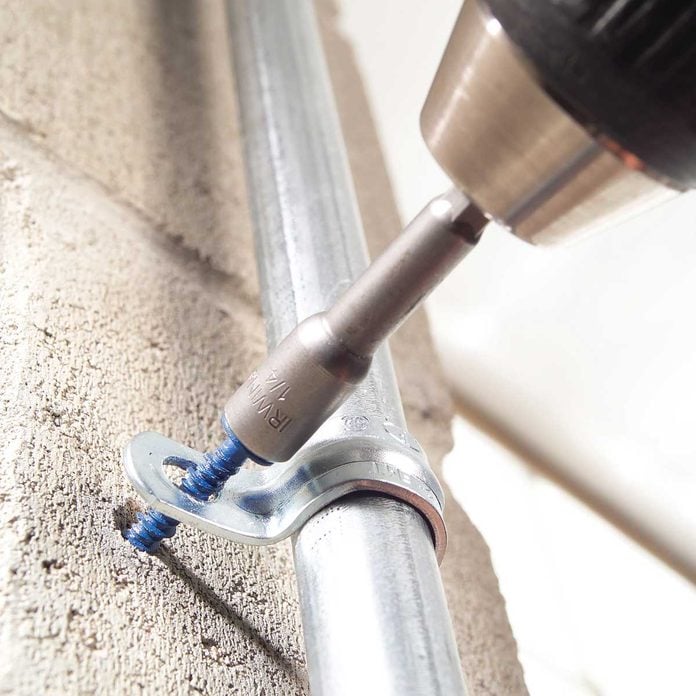
Concrete screws are available with either flat head Phillips or hex heads. In situations where the screw head must be flush to the surface (furring strips under drywall), or where a Phillips head would look nicer, use the Phillips head screws. Otherwise, always pick the hex head screws. The positive engagement of the hex bit makes them easier to drive (see photo, p. 35).You’ll need a 1/4-in. hex driver for the 3/16-in. screws and a 5/16-in. hex head driver for the thicker 1/4-in. screws.
When you’re using Phillips head screws, keep extra No. 2 (No. 3 for 1/4-in. screws) Phillips head bits on hand. The hardened screws wear out bits quickly.
Screw Heads and Usage
Drive Phillips head screws where a flush surface is required and where a Phillips head would look better. Otherwise use hex head screws.
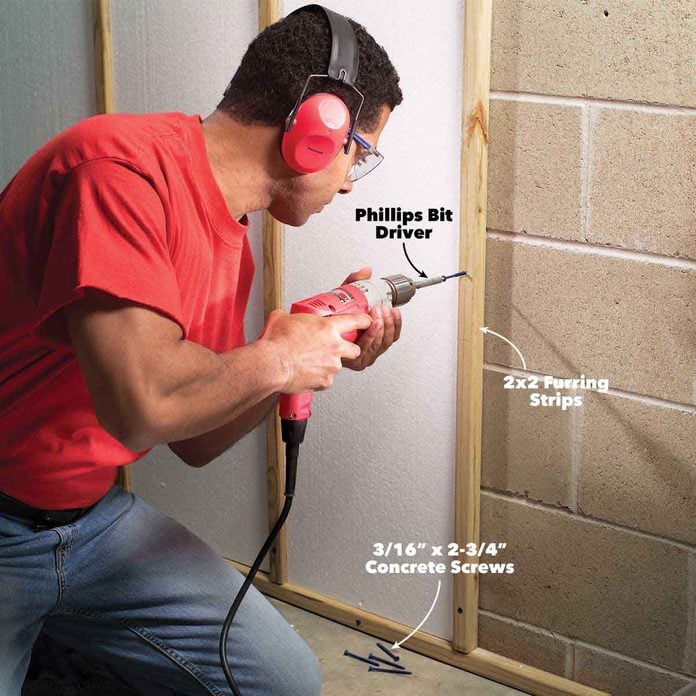

Drill With a Firm Hand and Maintain Steady Pressure
Good technique is essential for driving concrete screws. Not enough downward pressure and the bit could slip off the head, especially if you’re using Phillips head screws. For the best results, keep constant pressure on the screw and run the drill at slow to medium speed.
It takes a light touch to avoid snapping screws. Heavy-duty drills work best because they can maintain a steady slow speed. Stop as soon as the screw is flush to the surface and your material is firmly attached. Driving at high speeds results in overdriving the screw and can strip the threads or break off the head. You’ll develop a feel for the right amount of speed after driving a few screws.
Stopping Point
Ease off the driving speed as the screw head nears the surface.
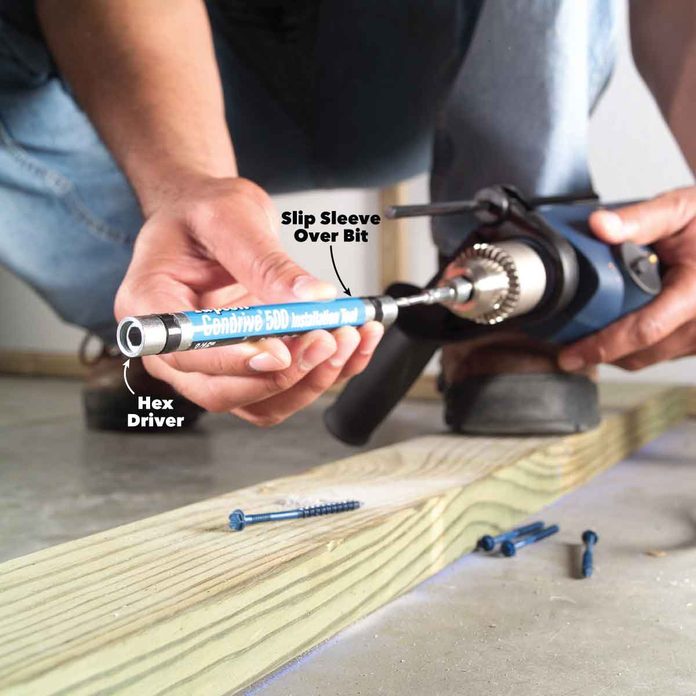

Use Two Drills or Buy an Installation Kit to Speed up the Job
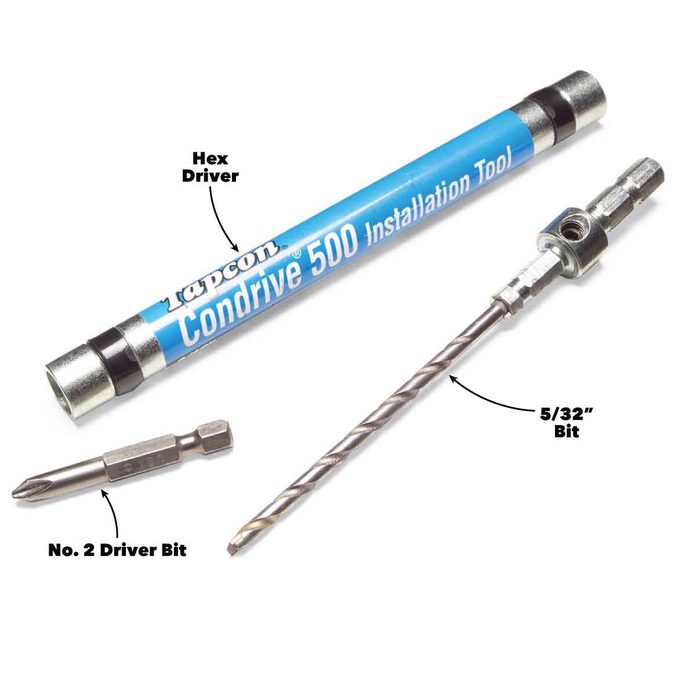
Install the masonry bit in your hammer drill and a driver bit in a variable speed drill. Then you won’t have to switch bits constantly. Another option is to buy an installation tool. It allows you to switch quickly from drilling to driving mode and back again, and includes Phillips and hex head bits to drive both 3/16-in. and 1/4-in. screws. We found an installation kit alongside the concrete screws at the home center.
Close-Up of Drill/Drive Kit
The kit contains a carbide-tipped bit (replaceable) a hex driver and a Phillips driver.
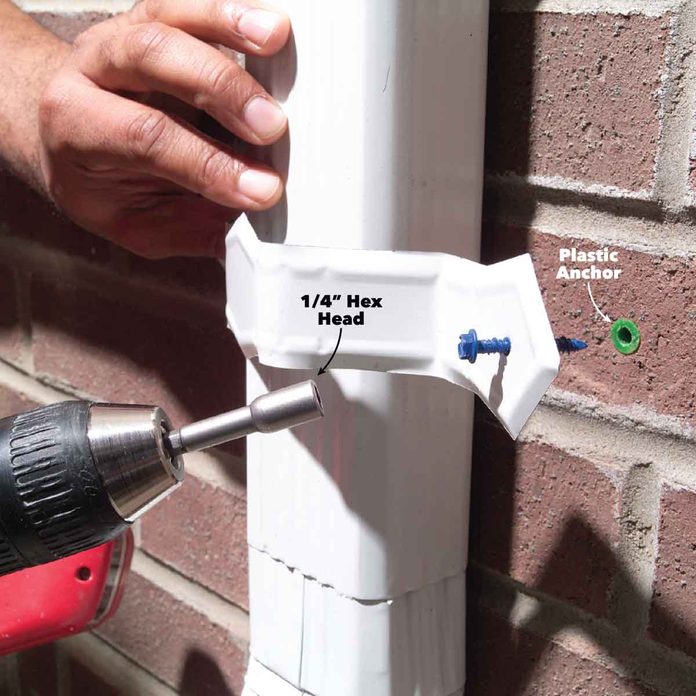

Keep a Handful of Plastic Anchors in Case of Strip-Out
Occasionally the threads of a screw won’t grip and the screw will spin in the hole. Usually you can just abandon this hole and drive another screw a short distance away. But if relocating the screw isn’t a good option, simply enlarge the hole and slip in a plastic anchor. Then drive the concrete screw into the anchor.
Sleeve Anchors for Concrete Block
Fastening heavy items to concrete block is simple if you use the right tools and fasteners. Where most people mess up is in thinking they can use plastic anchors. Uh, no. At the very least you should use a lag shield, but even then, you can use that type of anchor only when mounting to one of the three solid sections of the block.
Sleeve anchors are a better option because they work in the solid and hollow sections of the block, as well as the mortar joints. Here are two important tips when you’re installing sleeve anchors.
1. Leaving drilling dust in the hole will reduce the fastener’s holding power. So remove it with a vacuum or blower. A baby’s ear syringe (about $5 at any drugstore) works great for this (keep one in your toolbox). Just shove it into the hole and puff out the dust.
2. Protect the bolt threads by unscrewing the nut until it extends slightly past the bolt threads. Then drive it home with light hammer blows.



